Slot Waveguide Modulator
- Journal of the Optical Society of America B
- Vol. 29,
- Issue 6,
- pp. 1490-1496
- (2012)
- •https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.29.001490
- Share

In this paper, we analyse the performance of a silicon nano-opto-electro-mechanical system (NOEMS) applied as an optical modulator, based on a suspended slot waveguide driven by electrostatic forces. The analysis is carried out with the help of the finite element analysis (FEA) method involving the influences from Casimir force, optical force and electrostatic force. The performance of the. Epsilon-Near-Zero Si Slot-Waveguide Modulator Xiaoge Liu,† Kai Zang,‡ Ju-Hyung Kang,† Junghyun Park,† James S. Harris,‡ Pieter G. Kik,†,§ and Mark L. Brongersma.,† †Geballe Laboratory for Advanced Materials and ‡Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305, United States §CREOL, The College of Optics and Photonics, University of.
- Get CitationCopy Citation TextZhaolin Lu and Wangshi Zhao, 'Nanoscale electro-optic modulators based on graphene-slot waveguides,' J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29, 1490-1496 (2012)Export Citation
Abstract
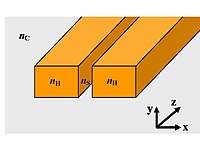
Research on graphene has revealed its remarkable electro-optic properties, which promise to satisfy the needs of future electro-optic modulators. However, its ultrasmall thickness, compared with operating light wavelength, downplays its role in an optoelectronic device. The key to achieve efficient electro-optic modulation based on graphene is to enhance its interaction with light. To this end, some novel waveguides and platforms will be employed to enhance the interaction. Herein, we present our recent exploration of graphene electro-optic modulators based on graphene sandwiched in dielectric or plasmonic waveguides. With a suitable gate voltage, the dielectric constant of graphene can be tuned to be very small due to the effect of intraband electronic transition, resulting in “graphene-slot waveguides” and greatly enhanced absorption modes. Up to 3 dB modulation depth can be achieved within 800 nm long silicon waveguides, or 120 nm long plasmonic waveguides based on three-dimensional numerical simulations. They have the advantages of nanoscale footprints, small insertion loss, low power consumption, and potentially ultrahigh speed, as well as being CMOS-compatible.
©2012 Optical Society of America
Full Article PDF ArticleOSA Recommended ArticlesSilicon Slot Waveguide
 Design of a graphene-based dual-slot hybrid plasmonic electro-absorption modulator with high-modulation efficiency and broad optical bandwidth for on-chip communication
Design of a graphene-based dual-slot hybrid plasmonic electro-absorption modulator with high-modulation efficiency and broad optical bandwidth for on-chip communicationZhongwei Wu and Yin Xu
Appl. Opt. 57(12) 3260-3267 (2018)
Abhijeet Phatak, Zhenzhou Cheng, Changyuan Qin, and Keisuke Goda
Opt. Lett. 41(11) 2501-2504 (2016)
Chao Xu, Yichang Jin, Longzhi Yang, Jianyi Yang, and Xiaoqing Jiang
Opt. Express 20(20) 22398-22405 (2012)
References
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Citation lists with outbound citation links are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Cited By
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Cited by links are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Figures (5)
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Figure files are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Metrics
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Article level metrics are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
- Optics Letters
- Vol. 41,
- Issue 11,
- pp. 2501-2504
- (2016)
- •https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.41.002501
- Share
- Get CitationCopy Citation TextAbhijeet Phatak, Zhenzhou Cheng, Changyuan Qin, and Keisuke Goda, 'Design of electro-optic modulators based on graphene-on-silicon slot waveguides,' Opt. Lett. 41, 2501-2504 (2016)Export Citation
Abstract
We present a graphene-on-silicon (GoS) suspended vertical slot waveguide. By changing the Fermi level of graphene, the variation in the effective refractive index (RI) of the waveguide is a factor of two larger than that in the traditional GoS rib waveguide. The improvement is due to the light-intensity enhancement and the poor confinement of the optical mode in the slot nanostructure. We design Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) and microring modulators based on the GoS suspended vertical slot waveguide. Our calculations show that the modulators can be energy-efficient and footprint-compact due to the large phase shift of the propagating mode in the waveguide after applying a gate voltage on the graphene. Fabrication of our design is easy and CMOS-compatible. It paves the way for chip-integrated electronic-RI modulators.
© 2016 Optical Society of America
Full Article PDF ArticleOSA Recommended ArticlesDesign of graphene-on-germanium waveguide electro-optic modulators at the 2μm wavelengthJiaqi Wang, Qiuxia Li, Dan Huang, Chongbin Liang, Yuzhi Chen, Lin Fang, Youfu Geng, Xueming Hong, and Xuejin Li
OSA Continuum 2(3) 749-758 (2019)
Hai Yan, Xiaochuan Xu, Chi-Jui Chung, Harish Subbaraman, Zeyu Pan, Swapnajit Chakravarty, and Ray T. Chen
Opt. Lett. 41(23) 5466-5469 (2016)
Slot Waveguide Modulator
Nanoscale electro-optic modulators based on graphene-slot waveguidesZhaolin Lu and Wangshi Zhao
J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29(6) 1490-1496 (2012)
References
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Citation lists with outbound citation links are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Cited By
Slot Waveguide Modulator Receiver
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Cited by links are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Figures (5)
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Figure files are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription

Waveguide Antenna
Equations (7)
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Equations are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Metrics
Slot Waveguide Modulator Switch

Plate-slot Polymer Waveguide Modulator On Silicon-on-insulator
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Article level metrics are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Slot Waveguide Modulator System
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription